Wireless communication technology requires a certain frequency band to communicate, just as a car needs to travel on the road. In the application of the Internet of Things, the frequency of wireless technology used in different countries or regions is also different. In order to adapt to the development of the Internet of Things, countries or regions provide certain frequency bands for IoT applications, as follows:
North America: 902-928MHz
EU: 863-868MHz
South Korea: 917.5-923MHz
Japan: 916.5-927.5MHz
United Kingdom: 915-921MHz
What are the frequency bands applicable to the Internet of Things market in China? In particular, what are the suitable bands for the emerging low-power wide area network (LPWAN) in China?
Frequency of wireless technology
If the wireless technology is divided according to the transmission distance, some common Internet of Things wireless technologies can be divided into the following:
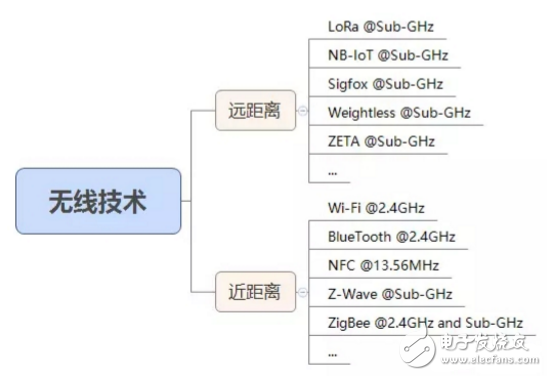
LoRa, China's LoRa Application Alliance (CLAA) recommends 470~510MHz.
NB-IoT, the world's mainstream frequency bands are 800MHz and 900MHz. China Telecom will use 800MHz as the preferred frequency band for deploying NB-IoT. China Unicom will choose 900MHz to deploy NB-IoT. China Mobile may re-cultivate the existing 900MHz frequency band.
Sigfox, Europe, Middle East: 868MHz (ETSI 300-220), North America: 902MHz (FCC part 15), South America/Australia/New Zealand: 920MHz (ANATEL 506, AS/NZS 4268).
Weightless, an open standard LPWAN wireless technology, operates over the entire unlicensed Sub-GHz ISM/SRD band and can be deployed globally: 169/433/470/780/868/915/923MHz.
ZETA, a technology developed by Latent Technology, can operate in multiple Sub-GHz bands (eg 433, 470, 500, 787, 868 and 915 MHz, etc.). In addition, ZETA can also be run on proprietary frequency bands by changing the configuration.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, working at 2.4GHz, the global frequency band.
NFC, it is reported that the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology will release the near field communication technology standard based on 13.56MHz.
Z-Wave, which operates at 868.40 MHz in China, complies with the CNAS/EN 300 220 standard.
ZigBee, Thread, ISA100.11a and other specifications are extended based on IEEE 802.15.4. The general IEEE 802.15.4 device uses 868/915/2400MHz frequency.
In addition to 2.4 GHz, etc., IoT wireless technologies are mostly based on the Sub-GHz band. What are the regulations and requirements for China's existing wireless spectrum?
Radio frequency regulations and requirements
There are several regulations, requirements and standards related to the Internet of Things:
"PRC Radio Frequency Division Regulations"
Technical Requirements for Micropower (Short Range) Radio Equipment
IEEE Std 802.15.4cTM-2009
Notice on Increasing the Operating Frequency of Micropower (Short Range) Radio Applications in the 800 MHz Band
Technical Requirements for Micropower (Short Range) Radio Equipment
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology revised and released the Technical Requirements for Micropower (Short Range) Radio Equipment in 2005. No. [2005] No. 423. The Requirements classifies 14 types of equipment:

Among them, (3) wireless microphones and civilian radio meters and other types of equipment
It is used for audio-visual training in education and culture departments, in public places such as cinemas, concert halls, conference rooms, and for hearing aids for people with disabilities. It is used as a small broadcasting device in tourist areas.
The 470-510MHz band can be used as a frequency band for civil radio meters when the transmission data is satisfied and its transmitter operating time is less than 5 seconds.
If the frequency of use is the same as the local sound and the frequency of the TV broadcast station, it should not be used locally; if it interferes with the local sound or TV broadcast reception, stop using it immediately, and then re-use it after eliminating the interference or adjusting to the interference-free frequency.
Guangzhou Fengjiu New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.flashfishbattery.com
