When the electrical equipment controlled by the inverter fails, first check the fault alarm information of the inverter, and determine the fault type according to the indication of the fault code. For example, the fault code such as overvoltage, undervoltage, and voltage loss can be judged to be faulty in the power supply loop. If the fault code such as overcurrent or overload is reported, the load condition can be checked, and the insulation resistance value of the motor and cable to the ground is shaken. If the communication is faulty, check the communication template, communication line and connectors of the inverter. The fault reset can be performed to restart the device after finding and eliminating the cause of the fault.
A network for providing control signals to a main circuit for supplying power to an asynchronous motor (voltage, frequency adjustable), called a control loop, a control circuit consisting of a frequency, a voltage operation circuit, a voltage of a main circuit, a current detection circuit, a speed detection circuit of a motor, A drive circuit that amplifies a control signal of an arithmetic circuit, and a protection circuit of the inverter and the motor. The speed-free detection circuit is open-loop control; the speed detection circuit is added to the control circuit, that is, the speed command is increased, and the speed of the asynchronous motor can be more accurately closed-loop controlled.
(1) The arithmetic circuit compares the external speed and torque commands with the current and voltage signals of the detection circuit to determine the output voltage and frequency of the inverter.
(2) The voltage and current detection circuit is isolated from the main circuit potential to detect voltage, current, and the like.
(3) The driving circuit is a circuit that drives the main circuit device, which is isolated from the control circuit to control the turning on and off of the main circuit device.
(4) The I/O circuit makes the frequency conversion better human-computer interaction, and it has the input of multiple signals (such as running multi-speed operation, etc.), and the input of various internal parameters (such as current, frequency, protection action drive, etc.). .
(5) The speed detecting circuit sets the signal of the speed detector (TG, PLG, etc.) mounted on the asynchronous motor shaft as a speed signal, and sends it to the arithmetic circuit to operate the motor at the command speed according to the command and calculation.
(6) The protection circuit detects the voltage, current, etc. of the main circuit. When an abnormality such as overload or overvoltage occurs, in order to prevent damage to the inverter and the asynchronous motor, the inverter is stopped or the voltage and current are suppressed.
The protection circuit in the inverter control circuit can be divided into two types: inverter protection and asynchronous motor protection. The protection functions are as follows:
(1) Inverter protection
1 Instantaneous overcurrent protection, used for inverter current load side short circuit, etc. When the current flowing through the inverter reversal reaches an abnormal value (exceeding the allowable value), the inverter is stopped instantaneously, the current is cut off, and the output of the converter is interrupted. When the current reaches an abnormal value, the inverter must also be stopped.
2 Overload protection, the inverter output current exceeds the rated value, and it continues to flow for more than the specified time. To prevent damage to the inverter components and wires, stop operation, proper protection requires inverse time characteristics, and use thermal relay or electronic thermal protection. The overload is caused by the GD2 (inertia) of the load being too large or the motor being blocked due to excessive load.
3 Regeneration overvoltage protection, when the inverter is used to make the motor decelerate rapidly, the DC circuit voltage rises due to the regenerative power, and sometimes exceeds the allowable value. It is possible to prevent the overvoltage by stopping the inverter operation or stopping the rapid method.
4 instantaneous power failure protection, the control circuit works normally for instantaneous power outage in milliseconds. However, if the instantaneous power failure is 10 ms or more, not only the control circuit malfunctions, but also the main circuit does not supply power, so the inverter is stopped after the detection.
5 Ground overcurrent protection, when the inverter load is grounded, in order to protect the inverter, there must be ground overcurrent protection. However, in order to ensure personal safety, it is necessary to install a leakage protection circuit breaker.
6 The cooling fan is abnormal. There is a device for cooling the fan. When the fan is abnormal, the temperature inside the device will rise. Therefore, the fan thermal relay or the device heat sink temperature sensor is used to stop the inverter after the abnormality is detected.
(2) Protection of asynchronous motor
1 Overload protection, the overload detection device is shared with the inverter protection, but when considering the overheating of the low speed operation, the temperature detector is buried in the asynchronous motor, or the electronic thermal protection installed in the inverter is used to detect the overheating. When the frequency is too high, consider reducing the motor load and increasing the capacity of the motor and inverter.
2 Overspeed protection, stop inverter operation when the output frequency of the inverter or the speed of the asynchronous motor exceeds the specified value
(3) Other protection
1 Prevent stall overcurrent. If the asynchronous motor tracks slowly during acceleration, the overcurrent protection circuit will operate and the operation will not continue (stall). Therefore, control should be performed before the load current is reduced to suppress the frequency rise or decrease the frequency. The same control is sometimes performed for overcurrent in constant speed operation.
(2) Preventing over-regeneration of over-voltage, the regenerative energy generated during deceleration increases the DC voltage of the main circuit, and prevents the regenerative over-voltage circuit from being operated. It is controlled before the DC voltage drops, suppressing the frequency drop and preventing the inability to operate (stall).
A through-bore slip ring is an electrical device that allows current to pass between two points in a rotating assembly without a physical connection. There is no break in the circuit. This is accomplished by passing the current through a rotating brush that contacts a stationary metal ring. The metal ring is mounted on the shaft of the assembly and provides a continuous path for the current.
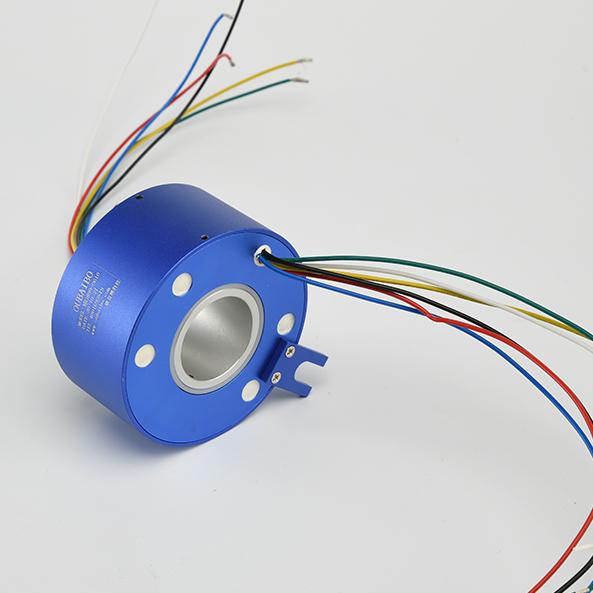
It is an integrated circuit component that consists of two conducting rings that are separated by a gap or spacer. When the rings are brought into contact, current can flow between them and produce a rotational motion. Slip rings are used in various applications where high efficiency and low power consumption are essential, such as communication systems, motor control systems, and energy harvesting devices.
The through-bore design allows for rotation of the assembly while transmitting power or data. They are often used in applications where there is a need to rotate an object while keeping a power or data connection open, such as on a wind turbine or radar antenna.
The Oubaibo's through-bore slip ring is a newly designed product that has many advantages over other products on the market. It is small and lightweight, making it easy to install and use. The through-bore design also allows for a high degree of flexibility, making it ideal for use in difficult or tight spaces. Additionally, the Oubaibo through-bore slip ring is very efficient, providing a high degree of power transfer with minimal loss.
Through-Bore Slip Ring,Slip Ring Connector,Power Slip Ring,Slip Ring Assembly
Dongguan Oubaibo Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sliprobs.com
