The coprocessor has a total of 68 different instructions. When the assembler encounters the coprocessor instruction mnemonic, it will convert it into a machine language ESC instruction. The ESC instruction represents the coprocessor's opcode.
When the coprocessor instruction needs to access the memory unit during execution, the CPU will form a memory address for it. The coprocessor uses the data bus to pass data during the execution of the instruction. The 80287 coprocessor uses the I/O address 00FAH~00FFH to exchange data with the CPU, while the 80387~PenTIum series chip uses the I/O address 800000FAH~800000FFH to implement data exchange between the two. .
Coprocessor three types of data transfer instruction data transfer instructionsIn order to meet the data exchange between the coprocessor and the CPU, it is necessary to implement instructions for data transfer between the memory unit and the coprocessor. There are three main types of data transfer instructions in the coprocessor's instruction system: BCD transfer instructions, floating point transfers, and integer transfer instructions.
First, BCD transfer instructions
1, FBLD
Instruction format: FBLD MemBCD(*)
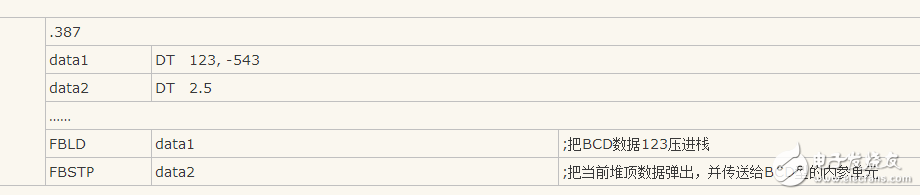
Instruction function: push the BCD data in the memory into the stack of the coprocessor;
(*) MemType is a memory unit that specifies the data type Type. For example, MemBCD is a BCD type storage unit. Will not be explained later.
2, FBSTP
Instruction format: FBSTP MemBCD
Instruction function: Store the BCD data in the coprocessor into the memory and perform the pop-up operation of the stack.
E.g:
Second, the floating point number transfer instruction

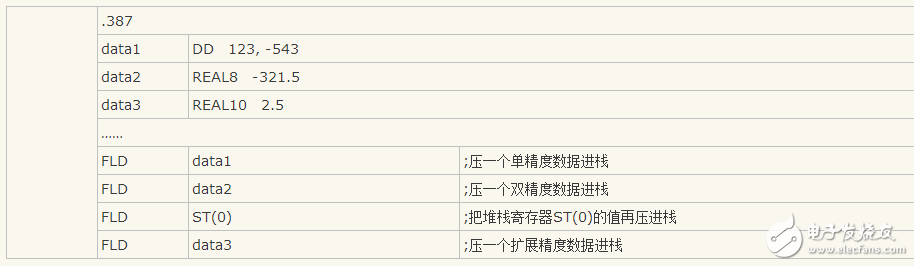
(*) STReg is the coprocessor stack registers ST(0)~ST(7).
E.g:
2, FST

3, FSTP

4, FXCH

For example: FXCH ST (2) - stack top data and stack register ST (2) for data exchange.
Third, the integer transfer instruction
1, FILD
Instruction format: FILD MemInt
Among them: MemInt is a memory unit defined as an integer data type, but it cannot be a storage unit defined by DB. The same below, no longer described.
2, FIST / FISTP

The difference between the instruction FIST and FISTP is the stack operation.
Membrane switch is an operating system that integrates key functions, indicating elements and instrument panels. It consists of four parts: panel, upper circuit, isolation layer and lower circuit.
When the membrane switch is pressed, the contacts of the upper circuit are deformed downward, and are in contact with the pole plate of the lower circuit.
After the finger is released, the contacts of the upper circuit bounce back, the circuit is disconnected, and the circuit triggers a signal. The membrane switch has strict structure, beautiful appearance and good sealing performance. It has the characteristics of moisture resistance and long service life.
Widely used in electronic communication, electronic measuring instruments, industrial control, medical equipment, automobile industry, smart toys, household appliances and other fields.
Can provide customers with professional product design. We HAVE accumulated MANY years of experience in Japanese customers, the company has stable quality management experience in mass production orders and can meet the customer's delivery time requirements and quality requirements on time. Now our products are widely used in communications, medical, electronics, digital, watches, automobiles and other high-end fields. With the ISO9001 factory certification, we have gradually become the industry leader with good management, leading technology, excellent quality, timely delivery and thoughtful service.
Membrane Switches, Poly Membrane Switches, Home Appliance Membrane Switch, Membrane Switch with Leds China Diy Membrane Switch
KEDA MEMBRANE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD , https://www.kedamembrane.com
