Data transmission rate, baud rate, symbol rate in digital communication
The data transmission rate and modulation rate in digital communication are two concepts that are easily confused. Data transmission rate (also known as code rate, bit rate, or data bandwidth) describes the number of bits of data code transmitted per second in communication, in bps. 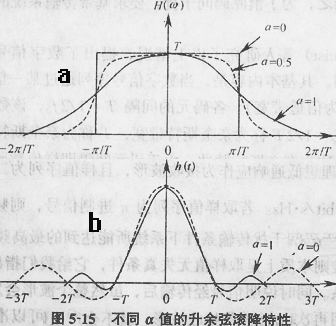
When the data is to be transmitted over a long distance, the data is often transmitted through modulation and demodulation technology, that is, the data signal is modulated on the carrier first, such as QPSK, various QAM modulation, etc., and then obtained by demodulation at the receiving end Data signal. The data signal will change various parameters of the carrier during the modulation of the carrier (amplitude change, phase change, frequency change, the presence or absence of the carrier, etc., depending on the modulation method). The baud rate describes the data signal to the analog In the process of carrier modulation, the value of the carrier changing every second is also called the modulation rate, and the baud rate is also called the symbol rate. In data modulation, the data is composed of symbols. With the different modulation techniques used, the number of bits mapped by the modulation symbols is also different. The symbol is also called unit symbol, which is the data information in a unit transmission period. If a unit symbol corresponds to two bits of data information (a binary number has two states 0 and 1, so it is two bits), then the symbol rate is equal to the bit rate; if a unit symbol corresponds to multiple bits For data information (m), the unit symbol is called a multi-ary symbol. At this time, the relationship between the bit rate and the symbol rate is: bit rate = symbol rate * log2 m, for example, QPSK modulation is a four-phase code, and one unit symbol corresponds to four bits of data information, that is, m = 4, then the bit rate = 2 * Symbol rate, here "log2 m" is also called the frequency band utilization, the unit is: bps / hz.
In addition, when the modulated signal is transmitted, the relationship between the symbol rate (SR) and the transmission bandwidth (BW) is: BW = SR (1 + α), α is the roll-off coefficient of the low-pass filter, when its value is 0 , With the highest frequency band utilization rate and the smallest occupied bandwidth, but due to the large fluctuation of the tail of the waveform (as shown in Figure 5-15b), it is easy to cause intersymbol interference; when its value is 1, the out-of-band characteristics are flat and occupy The maximum bandwidth is twice as long as 0; thus it can be seen that increasing the utilization rate of the frequency band contradicts \ "tailing \" convergence, so its value is generally not less than 0.15. For example, in a digital TV system, when α = 0.16, the bandwidth of an analog channel is 8M, then its symbol rate = 8 / (1 + 0.16) = 6.896Ms / s. If the 64QAM modulation method is used, then its bit rate = 6.896 * log2 64 = 6.896 * 6 = 41.376Mbps.

Follow WeChat

Download Audiophile APP

Follow the audiophile class
related suggestion
& n ...
![[Photo] Digital potentiometer IC DS1666](http://i.bosscdn.com/blog/20/06/41/7211949574.jpg)
![[Graphic] Digital watch 9V power supply replacement circuit](http://i.bosscdn.com/blog/20/06/41/6225911667.jpg)
![[Photo] Digital integrated circuit 5 watt transmitter](http://i.bosscdn.com/blog/20/06/41/5205329383.gif)
