The power rating of the power resistor of the first chapter is defined as the maximum power that can be consumed by the normal operation of the resistor under the specified ambient temperature , assuming that the air does not circulate. The specified ambient temperature is generally 25 ° C, 70 ° C, 125 ° C. It should be specially pointed out that the continuous normal operation of the resistor means that not only the resistor is not damaged, but also the resistance value of the resistor is within the allowable range.       Â
Usually we use the power reduction curve to describe the relationship between the power of the resistor and the ambient temperature. The higher the ambient temperature, the greater the resistance to heat dissipation of the resistor and the smaller the power. When the ambient temperature reaches the limit, the resistor loses its ability to dissipate heat and its power drops to zero.
Chapter II Classification of Power Resistors        Usually a resistor with a higher power rating can be called a power resistor. Divided into small power resistors and high power resistors according to different power levels. According to different materials and processes, power resistors are mainly divided into three categories: wire wound power resistors, membrane power resistors, and solid ceramic resistors.
Wirewound power resistors are the most common power resistors. Wirewound resistors are usually made of a resistor wire wound on a ceramic insulating substrate. The characteristics are simple process and economical price. The power of a single resistor can reach more than 3KW. The disadvantages are bulky, inductive, poor reliability, and uneven quality. The following are several common wirewound power resistors:

Membrane power resistors mainly refer to the planar power resistors of thick film technology. They are usually based on aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride substrate printing thick film resistor paste. These resistors have high power density and no sense of incompatibility, which is very suitable for space. Use in limited but good heat dissipation conditions. In addition, the wire-wound resistors have a wider range of resistance values, from milliohms to megohms. Membrane resistors are also defective. The first is that the overload capability is limited, and it is easily damaged in high-energy pulse applications such as discharge circuits, so the reliability is not high. In addition, the membrane resistors have high requirements for heat dissipation conditions, and a suitable heat sink must be added to achieve the rated power. Kaibu Electronics has introduced a planar power resistor based on power thin film technology, which is completely consistent with the thick film resistance in power density, and improves the reliability and stability of the resistor. The following are some common planar power resistors based on power thin film technology.

The manufacturing process of solid ceramic resistors is completely different from wirewound resistors and planar power resistors. After the powdery resistive materials are mixed, they are formed by molding, high-temperature sintering, electrode treatment, and final packaging test. The biggest difference between solid ceramic resistors and wirewound resistors and membrane planar power resistors is that they are electrically conductive, so they can withstand high energy and high pulse shock, which is very suitable for energy bleed, such as capacitor charging and discharging. Solid ceramic resistors have no sensation and high reliability. They are divided into power type and pulse type according to different applications.

Chapter 3 Common Mistakes in the Selection Process of Power Resistors (1) It is necessary to distinguish between high power and high pulse applications. In many applications, such as battery pack pre-charging, capacitor charging and discharging, starting current limiting, arc protection and other applications, the resistor does not need to work continuously for a long time under high power, but needs to withstand one or more periodic Pulse energy , best suited for this application is a high-energy pulse -resistant resistor instead of a high-power resistor. Of course, choosing a resistor with enough power may also satisfy this type of demand, but the potential risks remain. For example, high-power wirewound resistors only have resistive alloy wires that are electrically conductive. The weight of these resistive alloy wires is only a small fraction of the total resistance. When subjected to short-time high-pulse shocks, heat has no time to pass. The insulating substrate and the auxiliary heat sink are conducted out, so these very thin resistance wires themselves need to withstand a pulse of energy, which may result in direct damage or potential risk of electrical resistance. Many wirewound resistors are not designed for high-energy, high-pulse applications. Therefore, the actual pulse load is not taken into account in materials and processes. Once applied to a pulse circuit, it is prone to failure. At present, the most popular high-energy resistors are non-inductive solid ceramic resistors. In the high-energy pulse-resistant applications, this resistor saves more than 90% of the space compared to the wirewound resistor, and the reliability is improved by more than 10 times .

(2) The heat dissipation design is not emphasized, and the power space is reserved excessively or insufficiently. As we saw in the first chapter, the power of the resistor is its heat dissipation capability . The heat dissipation capability of the resistor can be improved by reasonable heat dissipation design, such as reasonable layout, installation of radiator, air cooling, water cooling, oil cooling and so on. Some resistors, especially planar power resistors, rely heavily on the heat sink. A planar power resistor in a TO220 package can be rated up to 50W with a reasonable heat sink, but with a heat sink of only 1.5. W.
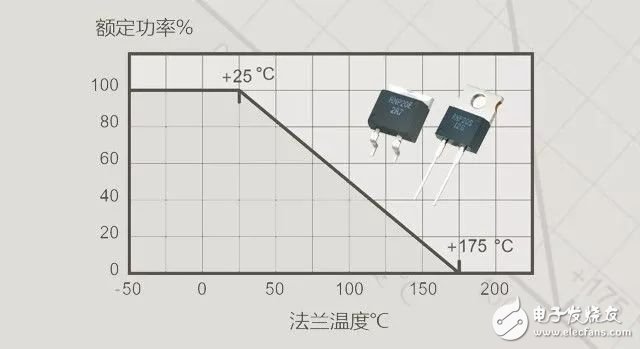
Most engineers derate the power resistors, which are usually deducted by half according to the military standard. Sometimes, in order to reduce heat, even further derating is needed. However, the amount of derating must be considered in combination with the working environment and heat dissipation conditions. For example, a power resistor with a rated power of 750W may be reduced to 500W when it is affected by the heat of the adjacent resistor, and cooled by air cooling (wind speed 150m/min). Can increase the power to 1000W. When the resistance heat sink is required in order to reach the nominal rated power, the general specifications will indicate power and power when the radiator does not increase with the increase with the radiator. Be sure to pay attention to these differences when selecting power resistors. (3) Insufficient estimation of the inductance of the wirewound resistor is known. The biggest defect of the wirewound resistor is the presence of inductance. A low inductance wirewound resistor can be obtained by the method of non-inductive winding, but it is not completely non-inductive. These inductances can be ignored in a few hundred hertz circuits. However, the wirewound resistor can no longer be used in high-frequency loads such as broadcast communication equipment. Both the membrane planar power resistor and the solid ceramic resistor can provide non-inductive characteristics. The parasitic inductance of these resistors is as low as nH. For example, the planar power resistor of the TO220 package produced by the open-step electronics has a series inductance lower than 10nH. In the application of high frequency and high pulse, not only the resistance is required to have non-inductive characteristics, but also the resistance of the resistor has high energy and anti-pulse characteristics. If the cost permits, the solid ceramic resistor is most suitable. (4) Choosing the right accuracy In this paper, we only discuss the power resistance of non-precision applications. While choosing a power resistor, accuracy is not an important indicator for most applications, but accuracy is by no means arbitrarily confirmed. Usually we recommend taking into account the initial accuracy and drift at the end of life, and then choose the accuracy based on the breadth principle . The principle of wide precision is not only conducive to cost savings, but more importantly, it can improve the reliability of the resistor, especially for the membrane resistor. This is because to achieve a higher precision, the membrane resistor must be adjusted, and the process of the resistance will damage the resistor layer, which will lose the rated energy of the resistor and reduce the overload capability of the resistor. Some wirewound resistor manufacturers will polish the wire to achieve the purpose of the regulation, which will reduce the overload capacity of the resistor by at least half. Therefore, the accuracy of the power resistor should be selected according to the principle of wideness. For example, when the accuracy of ±10% after the comprehensive evaluation can meet the requirements, it is not necessary to select the accuracy of ±5% or ±1%.
Desktop Multi-function Adapter is suitable for any normal brands Laptop. Wall Multi-function Adapter is suitable for people who always travel any country. Its plug is US/UK/AU/EU etc. We can produce the item according to your specific requirement. The material of this product is PC+ABS. All condition of our product is 100% brand new.
Our products built with input/output overvoltage protection, input/output overcurrent protection, over temperature protection, over power protection and short circuit protection. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
Multi-Function Adapter, 12W Wall Adapter, 30W Wall Adapter ,90W Desktop Adapter
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com
